Introduction to Demand Forecasting
In today’s fast-paced business environment, demand forecasting plays a critical role in driving smarter operations, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. By predicting future demand for products or services, organizations can optimize inventory, manage resources, and make proactive decisions that align with market needs.
Demand forecasting models are at the heart of this process. These models use historical data, market trends, and statistical methods to estimate future demand. From simple spreadsheet formulas to sophisticated AI-powered algorithms, choosing the right model can significantly impact accuracy and efficiency.
As industries evolve and data becomes more accessible, companies are rethinking traditional forecasting techniques. Enter AI-based demand forecasting models—smarter, faster, and more adaptable to real-world complexity.
Why AI Matters in Forecasting Today
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming demand forecasting from a static, backward-looking function into a dynamic, real-time decision-making capability. While traditional models rely on fixed assumptions and structured data, AI models can process vast, unstructured datasets and identify patterns that humans may miss.
Why is this shift important? Markets today are more volatile than ever. Consumer behavior is unpredictable, supply chains are global and fragile, and external factors—like inflation, weather, or geopolitical shifts – can impact demand overnight. Traditional demand forecasting models often struggle to adapt quickly to these variables.
AI-driven forecasting offers several key advantages:
- It automates model selection and tuning
- It continuously learns from new data
- It adjusts predictions based on real-time signals
As a result, organizations can reduce forecast error, improve responsiveness, and make decisions with greater confidence.
Traditional vs. AI Forecasting Approaches
For decades, businesses have relied on statistical forecasting techniques like moving averages, exponential smoothing, and ARIMA to project future demand. These models, known as traditional demand forecasting models, are grounded in time-series analysis and work best when historical patterns are stable, linear, and predictable. These models have major limitations in today’s dynamic and highly volatile environments.
Limitations of Traditional Forecasting Models
- Rigid Assumptions
Traditional models assume linearity and stationarity in data—meaning they expect demand to follow consistent trends over time. This makes them less effective when abrupt changes happen due to promotions, supply chain disruptions, or external events.
- Minimal External Input
These models typically focus only on internal data (like past sales) and ignore external variables such as weather, inflation, social trends, or competitor actions, which are increasingly influential in shaping demand.
- Manual Effort and Tuning
Models like ARIMA require data scientists or analysts to manually tune parameters (p, d, q), validate outputs, and periodically retrain the model—creating a bottleneck in fast-paced business environments.
- Limited Scalability
Traditional forecasting tools struggle to scale across thousands of SKUs, multiple regions, or product hierarchies without a significant increase in complexity and human oversight.
- Slow Response to Change
When faced with abrupt demand shifts—such as those caused by COVID-19, market entry of a competitor, or logistical delays—traditional models often fail to adapt quickly, resulting in inaccurate forecasts and business losses.
The Rise of AI-Based Demand Forecasting Models
To address these challenges, businesses are increasingly turning to AI demand forecasting models. Unlike traditional methods, AI models leverage machine learning algorithms that can detect complex, nonlinear patterns and dynamically learn from new data over time.
These models don’t just rely on what happened in the past—they continuously adjust predictions based on what’s happening now and what’s likely to happen next. AI forecasting tools can incorporate a wide range of variables, including:
- Promotional calendars
- Regional weather data
- Social sentiment
- Supplier performance
- Macroeconomic indicators
- Competitor pricing and stock levels
This multi-variable modeling allows organizations to move beyond simple trend projection and build a more realistic, nuanced picture of future demand.
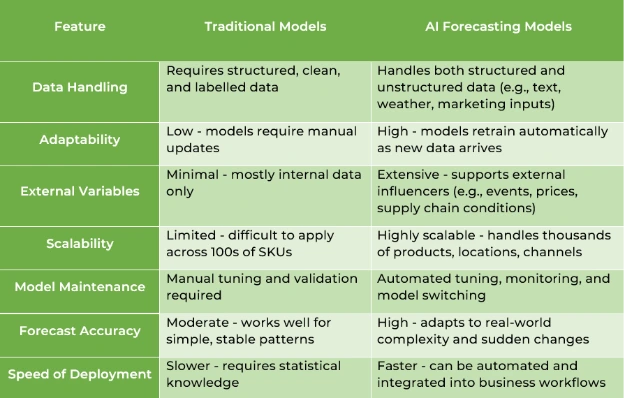
Comparative Breakdown
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of key capabilities:
Key AI Forecasting Models
AI brings a diverse and powerful toolkit of forecasting models, each designed to address different levels of complexity, data structures, and business contexts. Whether you’re managing predictable retail sales or navigating the uncertainties of global supply chains, choosing the right AI demand forecasting model can dramatically enhance your forecast accuracy, responsiveness, and scalability.
Below are three of the most widely adopted and effective AI-driven demand forecasting models in modern business applications:
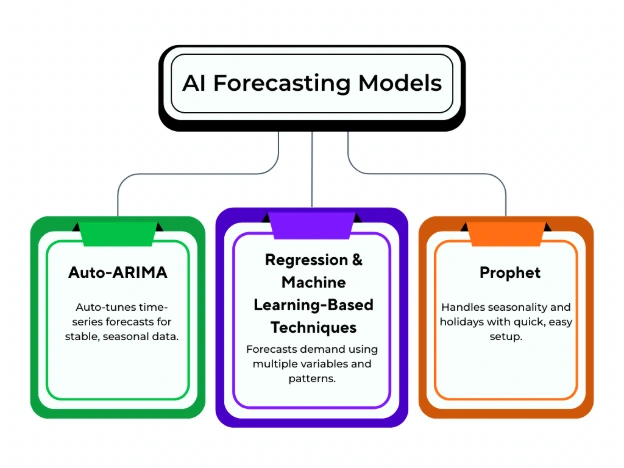
Auto-ARIMA (Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average)
Auto-ARIMA is an intelligent extension of the classical ARIMA model, which has long been used for time-series forecasting. While standard ARIMA models require manual selection of parameters (p, d, q) and can be sensitive to incorrect assumptions, Auto-ARIMA automates the entire model selection and tuning process. This significantly reduces the time, expertise, and trial-and-error effort needed to build a reliable model.
Best suited for:
- Time-series data with consistent trends and seasonal patterns
- Forecasting in environments with relatively stable demand behavior (e.g., utilities, office supplies, MRO inventory)
Advantages:
- Automated parameter optimization using AIC/BIC criteria
- Good short-to-medium-term forecast performance
- Interpretable outputs for business reporting
- Works well with univariate datasets (i.e., using only historical demand)
Limitations:
- Assumes linear relationships and constant variance
- Not responsive to real-time external influencers like promotions, holidays, or market disruptions
- Less effective when data shows abrupt changes or irregular trends
Auto-ARIMA remains a strong option when forecasts need to be fast, reliable, and low on complexity—especially when paired with tools that automate deployment at scale.
Prophet
Prophet is an open-source time-series forecasting library developed by Facebook. It was designed with business users in mind and is known for being easy to use, highly interpretable, and effective in capturing seasonality, holiday effects, and trend shifts.
Prophet models the time series as a combination of trend, seasonality, and holiday impact components, which makes it particularly well-suited for businesses with cyclical or seasonal patterns.
Best suited for:
- Retail and e-commerce companies dealing with promotions, holidays, or weekly demand fluctuations
- Logistics and delivery services with daily or hourly planning cycles
- Marketing campaign performance forecasting
Advantages:
- Built-in support for custom seasonality and recurring events
- Handles missing data and outliers gracefully
- Requires minimal data preprocessing
- Provides confidence intervals for risk assessment
- Fast, interpretable, and easy to fine-tune
Limitations:
- Less suitable for data with high dimensionality or complex dependencies
- Doesn’t naturally handle multiple influencing variables (external regressors must be manually added)
- May underperform on highly irregular or abrupt demand shifts without external features
Prophet strikes an excellent balance between usability and power—especially for business teams looking for fast deployment and accurate forecasts with minimal complexity.
Regression & Machine Learning-Based Techniques
This category includes a broad set of supervised learning algorithms that can model relationships between demand and one or more influencing variables. Some popular models include:
- Linear Regression: Simple and interpretable, used when relationships are well understood
- Random Forests: Ensemble learning method using decision trees, good for nonlinear relationships
- Gradient Boosting Machines (XGBoost, LightGBM): High-performing models for structured tabular data
- Neural Networks and LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory): Deep learning models designed for sequential data and long-term dependencies
These techniques allow demand forecasting models to go beyond historical patterns by incorporating a wide range of internal and external factors, including:
- Weather data
- Economic indicators
- Promotional campaigns
- Product pricing
- Competitor activity
- Social media trends
Best suited for:
- Complex, multivariate forecasting across large product catalogs or regions
- Industries with high demand volatility, such as fashion, electronics, or FMCG
- Enterprises aiming to integrate AI across the planning and analytics stack
Advantages:
- Handles high-dimensional and nonlinear relationships with ease
- Supports real-time learning and adaptation
- Capable of multi-step forecasting (e.g., next week, next month, next quarter)
- Scalable across thousands of SKUs and geographic zones
Limitations:
- Requires large, labeled datasets for training
- Computationally intensive—may require GPU or cloud infrastructure
- Often seen as a “black box” unless explainability tools are built in
- Needs ongoing model maintenance and performance monitoring
Machine learning techniques offer unmatched flexibility and performance but require careful implementation, governance, and alignment with business workflows. Many companies are now using hybrid models—blending traditional and AI models—to balance accuracy, transparency, and usability.
How to Select the Right Model
Choosing the right demand forecasting model depends on several key factors:
- Data Volume and Quality: Large, clean datasets support more complex models like deep learning, while smaller datasets may require simpler approaches.
- Forecasting Horizon: Short-term forecasts (days/weeks) may use traditional models, while long-term forecasts (months/quarters) benefit from AI models.
- Demand Volatility: Highly variable or seasonal demand is better handled by AI forecasting models with adaptive learning capabilities.
- Business Use Case: Choose based on your operational goal—inventory planning, sales forecasting, labor planning, etc.
- Resources and Skill Sets: Some models require data science expertise, while others are built for business users with no-code interfaces.
To make this process easier, companies can use a model selection matrix or a decision tree framework to map their needs to the most appropriate demand forecasting model.
Benefits of Using AI in Forecasting
Adopting AI-based demand forecasting models offers several strategic advantages:
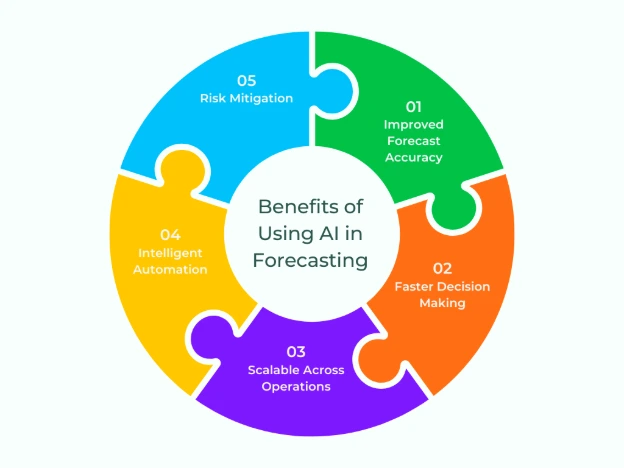
- Improved Forecast Accuracy: AI models adapt to changes in trends, behaviors, and external conditions in real time, reducing forecast error significantly.
- Faster Decision Making: With real-time processing and automated insights, businesses can respond faster to demand changes—reducing lead times and missed opportunities.
- Scalable Across Operations: AI models can be deployed across thousands of SKUs, locations, or product categories—something traditional models struggle to handle efficiently.
- Intelligent Automation: AI automates repetitive tasks such as data preprocessing, feature selection, and model tuning—freeing up analysts for higher-value tasks.
- Risk Mitigation: Scenario modeling, what-if analysis, and exception alerts help companies proactively manage supply risks, disruptions, and demand surges.
ConverSight AI Demand Forecasting Models
ConverSight offers a comprehensive suite of AI demand forecasting models through its intelligent, enterprise-ready Decision Intelligence platform—purpose-built to serve the dynamic needs of manufacturers, retailers, and distributors. Whether you’re managing thousands of SKUs, responding to seasonal demand, or aligning production with shifting customer preferences, ConverSight enables smarter, faster, and more adaptive forecasting.
At the core of ConverSight’s forecasting capabilities is a robust engine powered by machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and predictive analytics, enabling teams to move beyond static spreadsheets and outdated tools.
Key features include:
- Pre-built forecasting templates tailored to common industry use cases, enabling rapid deployment with minimal configuration.
- A powerful combination of Auto-ARIMA, Prophet, and advanced ML-based model ensembles, selected dynamically based on your business data and forecasting goals.
- Seamless ERP and supply chain integration, ensuring forecasts are always driven by the most up-to-date operational and transactional data.
- Built-in scenario planning and what-if simulations, helping users evaluate the impact of variables like pricing changes, supplier delays, and market shifts before making decisions.
- Conversational AI assistant, Athena, which allows users to query forecasts, trends, and KPIs using plain language—making advanced analytics accessible to business users without technical expertise.
- Continuous learning loops, which automatically retrain models based on new data inputs, so your forecasts evolve with your business—without requiring constant manual intervention.
Whether you’re managing seasonal retail sales, complex production schedules, or multi-region inventory, ConverSight’s models are tailored to your specific industry use case—helping you forecast with confidence. Want to explore how AI demand forecasting models can transform your business? Download Our Whitepaper to learn more.
Conclusion
Demand forecasting is evolving rapidly, and businesses that fail to modernize their approach risk falling behind. While traditional models have their place, AI demand forecasting models offer unmatched agility, accuracy, and scalability in a complex, fast-moving world.
By understanding the strengths of each model—Auto-ARIMA for simplicity, Prophet for seasonality, and ML techniques for complexity—organizations can build a robust forecasting strategy. Platforms like ConverSight make it easy to access the power of AI without the need for a large data science team. Learn more about ConverSight’s AI demand forecasting solution.
The future belongs to businesses that use demand forecasting not just as a planning tool—but as a strategic advantage.







